4.java并发编程基础
大约 3 分钟
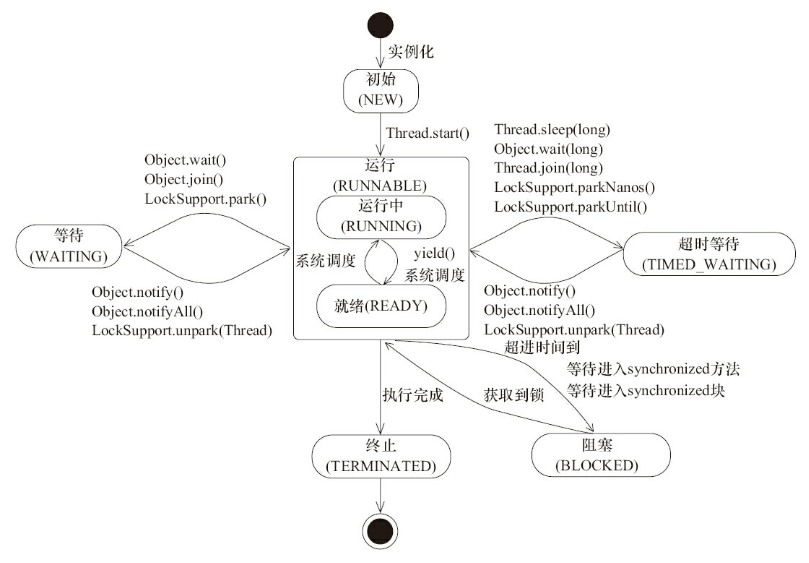
java线程状态 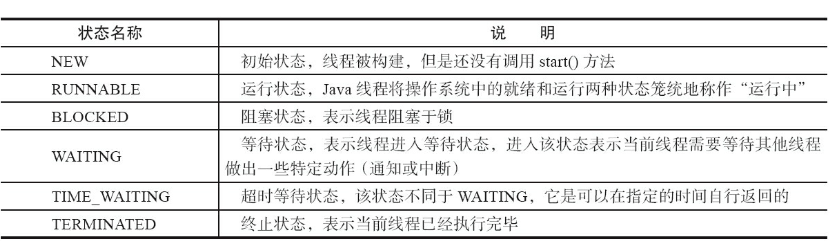
查看线程状态
public class ThreadState {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(new TimeWaiting(), "TimeWaitingThread").start();
new Thread(new Waiting(), "WaitingThread").start();
// 使用两个Blocked线程,一个获取锁成功,另一个被阻塞
new Thread(new Blocked(), "BlockedThread-1").start();
new Thread(new Blocked(), "BlockedThread-2").start();
}
// 该线程不断地进行睡眠
static class TimeWaiting implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
sleep(100);
}
}
}
// 该线程在Waiting.class实例上等待
static class Waiting implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
synchronized (Waiting.class) {
try {
Waiting.class.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
// 该线程在Blocked.class实例上加锁后,不会释放该锁
static class Blocked implements Runnable {
public void run() {
synchronized (Blocked.class) {
while (true) {
sleep(100);
}
}
}
}
public static void sleep(long seconds) {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(seconds);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
}
}
线程优先级不能正确执行 Daemon线程 finally 块代码不能清理做清理或关闭逻辑 中断 interrupt:是一个线程的标识位
优雅的终止线程
class Runner implements Runnable {
private volatile boolean on = true;
@Override
public void run() {
//中断退出
while (on && !Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()){ //循环判断
// todo working
}
}
//关闭线程
public void cancel(){
on = false;
}
}
$ jps
935 Jps
929 ThreadState
$ jstack 929
Daemon线程
Daemon线程是一种支持型线程,因为它主要被用作程序中后台调度以及支持性工作
Daemon线程被用作完成支持性工作,但是在Java虚拟机退出时Daemon线程中的finally块并不一定会执行
public class Daemon {
public static void main(String[] args){
Thread thread = new Thread( new DaemonRunner(),"DaemonRunner" );
thread.setDaemon( true );
thread.start();
}
static class DaemonRunner implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep( 10_000L );
}catch (Exception e){
}finally {
//finally 不一定执行
System.out.println("DaemonRunner is finish");
}
}
}
}
优雅停止线程
中断和标识位
/**
* 优雅退出线程
*/
public class Shutdown {
static class Runner implements Runnable {
private volatile boolean on = true;
@Override
public void run() {
//中断退出
while (on && !Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()){ //循环判断
// todo working
}
}
//关闭线程
public void cancel(){
on = false;
}
}
}
线程间通信
- volatile和synchronized关键字
- 等待/通知机制
- 管道输入/输出流
- Thread.join() 等待返回
- ThreadLocal
生产者-消费者
public class ProduceAndConsume {
private Object lock = new Object();
private volatile boolean flag = true;
private volatile int i = 0;
//生产者
public void produce() {
synchronized (lock) {
//todo 代码执行逻辑
i = i + 1;
System.out.println( "produce: + 1 " + i );
flag = false;
lock.notifyAll();
}
}
//消费者
public void consume() {
synchronized (lock) {
while (flag) {
try {
//线程进入waitting状态, 会释放对象锁
lock.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
flag = true;
//todo 执行逻辑
i = i - 1;
System.out.println( "consume: -1 " + i );
}
}
public void consumeWait(long mills) {
synchronized (lock) {
long future = System.currentTimeMillis() + mills;
long remaining = mills;
while (remaining > 0) {
try {
lock.wait( remaining );
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return;
}
remaining = future - System.currentTimeMillis();
}
//todo 执行代码
}
}
}
管道读写
public class Piped {
private PipedWriter out;
private PipedReader in;
public Piped() {
out = new PipedWriter();
in = new PipedReader();
//输入流于输出进行连接 否则在使用时会抛出IOException
try {
out.connect( in );
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void write() throws IOException {
int receive = 0;
//读取 系统输入流
while ((receive = System.in.read()) != -1) {
out.write( receive );
}
}
public void read() throws IOException {
int receive = 0;
while ((receive = in.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print( (char) receive );
}
}
public void close(){
try {
out.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public void testPipe() {
final Piped piped = new Piped();
Thread thread1 = new Thread( new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
piped.write();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
} );
Thread thread2 = new Thread( new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
piped.read();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
} );
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
try {
thread1.join();
thread2.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
piped.close();
}
}
join实现
public final synchronized void join() throws InterruptedException {
// 条件不满足,继续等待
while (isAlive()) {
wait(0);
}
}
ThreadLocal
public class Profiler {
private static final ThreadLocal<Long> TIME_THREAD_LOCAL = new ThreadLocal<Long>();
public static void begin(){
TIME_THREAD_LOCAL.set( System.currentTimeMillis() );
}
public static long end(){
return System.currentTimeMillis() - TIME_THREAD_LOCAL.get();
}
}